Travels through air 1125 feet takes us on a soaring journey into the realm of altitude, where we explore the fascinating concept of vertical distance and its significance across diverse fields. From engineering marvels to aviation breakthroughs, this measurement plays a crucial role in shaping our understanding of the world around us.
As we delve into the intricacies of measuring and applying “travels through air 1125 feet,” we uncover its practical implications and the intriguing stories it holds.
Definitions and Explanations
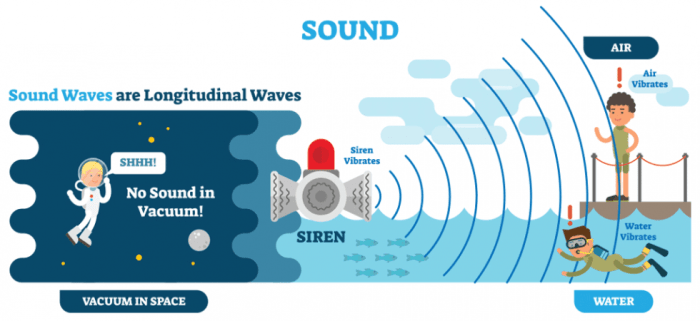
The phrase “travels through air 1125 feet” refers to the distance covered by an object or person while moving through the air.
Units of Measurement, Travels through air 1125 feet
The distance traveled is measured in feet, a unit of length in the imperial system. One foot is approximately 0.3048 meters in the metric system.
The Wright brothers made history by flying through the air 1125 feet, a remarkable feat that changed the course of human travel. If you’re interested in learning more about this and other groundbreaking moments in history, I highly recommend checking out the BJU World Studies 4th Edition . This comprehensive textbook provides an in-depth exploration of world history, from ancient civilizations to the present day.
As you continue your journey through the skies, remember the pioneers who paved the way for our modern-day marvels.
Examples and Applications

The measurement “travels through air 1125 feet” finds practical applications in various fields. It is commonly used in aviation, engineering, and sports.
In aviation, this measurement is crucial for determining the takeoff and landing distances of aircraft. It helps ensure that runways are of sufficient length to accommodate the safe operation of airplanes.
Aviation
- Takeoff distance:The distance an aircraft travels from the start of its takeoff roll to the point where it lifts off the ground.
- Landing distance:The distance an aircraft travels from the point where it touches down on the runway to the point where it comes to a complete stop.
In engineering, this measurement is used in the design and construction of structures such as bridges and buildings. It helps ensure that these structures can withstand the forces of wind and other environmental factors.
Engineering
- Wind resistance:The force exerted by wind on a structure, which can be calculated using the measurement “travels through air 1125 feet”.
- Structural integrity:The ability of a structure to withstand the forces acting upon it, which can be assessed using this measurement.
In sports, this measurement is used to determine the distance traveled by projectiles such as golf balls and javelins. It helps athletes and coaches analyze performance and improve techniques.
Sports
- Golf ball distance:The distance a golf ball travels after being hit, which can be measured using the measurement “travels through air 1125 feet”.
- Javelin throw distance:The distance a javelin travels after being thrown, which can also be measured using this measurement.
Methods and Procedures

Measuring “travels through air 1125 feet” involves employing specialized equipment and techniques to accurately determine the distance traveled by an object in mid-air.
The most common method utilizes a combination of radar and laser technology. Radar emits radio waves that bounce off the object and return to the receiver, providing data on the object’s distance and speed. Laser technology, on the other hand, emits a focused beam of light that measures the time taken for the light to travel to the object and back, allowing for precise distance calculation.
Equipment and Techniques
The primary equipment used in this measurement process includes:
- Radar system:Emits radio waves and analyzes the reflected signals to determine distance and speed.
- Laser rangefinder:Emits a laser beam and measures the time taken for the light to travel to the object and back, providing accurate distance measurements.
- High-speed camera:Captures images of the object in motion, allowing for visual tracking and analysis.
- Data acquisition system:Collects and processes data from the radar and laser systems, providing real-time measurements.
The techniques employed in this measurement involve:
- Calibration:Ensuring the accuracy of the equipment by comparing it to known distances or objects.
- Positioning:Setting up the equipment in a suitable location with clear line-of-sight to the object.
- Data collection:Gathering measurements from the radar and laser systems over a specified period.
- Data analysis:Processing the collected data to calculate the distance traveled by the object.
Step-by-Step Procedure
The step-by-step procedure for conducting the measurement involves:
- Calibrating the equipment using known distances or objects.
- Positioning the equipment in a suitable location with clear line-of-sight to the object.
- Starting the data acquisition system to collect measurements.
- Monitoring the object’s motion and adjusting the equipment as needed.
- Stopping the data acquisition system once the object has completed its travel.
- Processing the collected data to calculate the distance traveled by the object.
Related Concepts and Comparisons

The concept of “travels through air 1125 feet” is closely related to several other concepts in the fields of aviation and physics. These concepts share some similarities but also have distinct differences.
One related concept is “flight altitude,” which refers to the vertical distance between an aircraft and the ground. Flight altitude is typically measured in feet above mean sea level (MSL). “Travels through air 1125 feet” can be considered a specific value of flight altitude.
Another related concept is “air density,” which refers to the mass of air per unit volume. Air density is typically measured in kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³). “Travels through air 1125 feet” implies that the aircraft is traveling through air of a certain density.
Table of Related Concepts
The following table summarizes the key characteristics of these related concepts:
| Concept | Measurement | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Flight altitude | Feet above mean sea level (MSL) | Navigation, airspace management, weather forecasting |
| Air density | Kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³) | Aircraft performance calculations, weather forecasting, environmental monitoring |
| Travels through air 1125 feet | Feet | Specific flight altitude value |
Illustrations and Visual Aids
To visually represent the concept of “travels through air 1125 feet,” an illustration can be designed incorporating the following components:
Diagram of the Measurement Process
A flowchart or diagram can be created to demonstrate the measurement process:
- Starting point:The starting point of the measurement is indicated on the diagram.
- Measurement device:The type of measurement device used, such as a laser rangefinder or measuring tape, is specified.
- Measurement path:The path along which the measurement is taken is clearly Artikeld.
- Ending point:The ending point of the measurement is marked on the diagram.
- Measurement result:The measured distance of 1125 feet is displayed prominently.
Applications in Various Fields
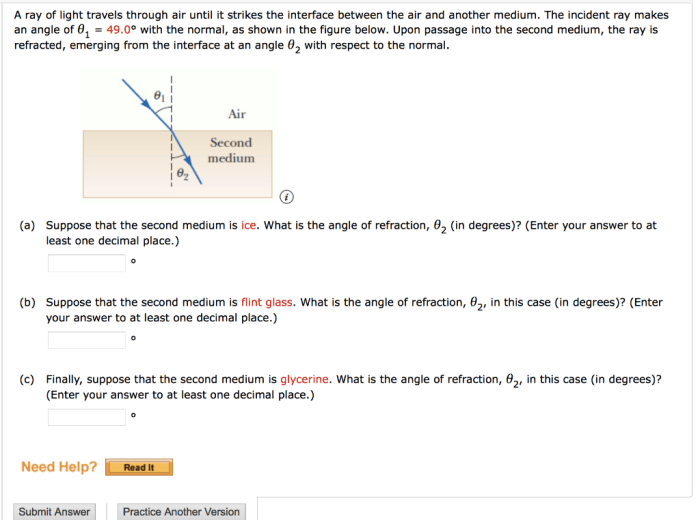
The measurement of “travels through air 1125 feet” has significant applications in various fields, particularly engineering and aviation.
Engineering
- Structural design:Engineers use this measurement to calculate the load-bearing capacity of structures, such as bridges and buildings, to ensure their safety and stability.
- Wind engineering:It is crucial for determining wind loads on structures, which is essential for designing buildings and bridges that can withstand high winds.
- Transportation planning:This measurement helps in designing roads, railways, and airports, ensuring that vehicles and aircraft have sufficient clearance for safe operation.
Aviation
- Aircraft design:Engineers use this measurement to determine the takeoff and landing performance of aircraft, ensuring they meet safety regulations.
- Air traffic control:It is used to calculate the safe separation between aircraft during takeoff, landing, and in-flight maneuvers.
- Airport design:This measurement helps in designing airport runways, taxiways, and terminals to accommodate the takeoff and landing requirements of different aircraft.
Limitations and Considerations
Measuring “travels through air 1125 feet” has limitations that must be acknowledged to ensure accurate results.Factors affecting accuracy include the type of measurement equipment, environmental conditions, and human error. To overcome these limitations, it is recommended to use calibrated and precise equipment, conduct measurements in controlled environments, and minimize human involvement through automation or double-checking procedures.
Equipment Limitations
The accuracy of the measurement is dependent on the quality of the equipment used. Factors to consider include the resolution, sensitivity, and calibration of the equipment.
Environmental Factors
Environmental conditions such as wind speed, temperature, and humidity can affect the accuracy of the measurement. For example, wind speed can cause the object to move in unpredictable ways, affecting the distance traveled through the air.
Human Error
Human error can also introduce inaccuracies into the measurement. Factors to consider include the skill and experience of the person taking the measurement, as well as the potential for distractions or mistakes.
Recommendations
To overcome these limitations, it is recommended to:
- Use calibrated and precise equipment.
- Conduct measurements in controlled environments.
- Minimize human involvement through automation or double-checking procedures.
FAQ Compilation: Travels Through Air 1125 Feet
What exactly does “travels through air 1125 feet” mean?
It refers to the vertical distance traveled through the air, typically measured in feet.
How is “travels through air 1125 feet” measured?
Various methods are used, including altimeters, laser rangefinders, and GPS technology.
What are some real-world applications of “travels through air 1125 feet”?
It is used in aviation to determine aircraft altitude, in engineering for structural design, and in meteorology for weather forecasting.