With tricks to lower HC emissions at the forefront, this paragraph opens a window to an amazing start and intrigue, inviting readers to embark on a storytelling journey filled with unexpected twists and insights.
HC emissions pose a significant environmental and health hazard, and understanding how to reduce them is crucial. This guide delves into the nature, sources, and impacts of HC emissions, providing a comprehensive overview of effective methods, technological advancements, and best practices for their control.
Overview of HC Emissions
Hydrocarbon (HC) emissions are composed of unburned fuel and partially burned fuel components that escape from vehicle engines, industrial processes, and other sources. These emissions contribute significantly to air pollution and pose various environmental and health risks.
Sources of HC Emissions
- Vehicle exhaust:Incomplete combustion of fuel in gasoline and diesel engines releases HC emissions.
- Industrial processes:Chemical manufacturing, petroleum refining, and solvent use emit HCs as byproducts.
- Fuel evaporation:Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in gasoline and other fuels evaporate during storage and transportation, contributing to HC emissions.
- Natural sources:Vegetation, wildfires, and biological processes release HCs into the atmosphere.
Environmental and Health Impacts of HC Emissions
HC emissions contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog, which can cause respiratory problems, eye irritation, and damage to crops and ecosystems. Additionally, some HCs are known carcinogens and can increase the risk of cancer.
Methods for Lowering HC Emissions
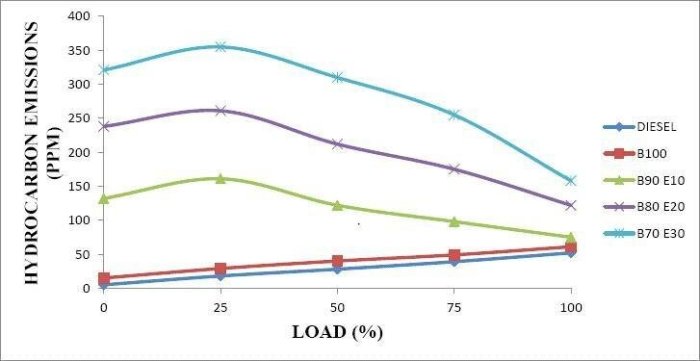
Hydrocarbon (HC) emissions, primarily released by vehicles, contribute to air pollution and pose significant environmental and health concerns. Implementing effective strategies to reduce HC emissions is crucial for improving air quality and mitigating their adverse impacts.
Various methods can be employed to lower HC emissions, each with its unique mechanism and effectiveness. Understanding these methods and their applications is essential for policymakers, industry professionals, and individuals seeking to reduce their carbon footprint.
Catalytic Converters
Catalytic converters are devices installed in vehicle exhaust systems that convert harmful pollutants, including HCs, into less harmful substances. They utilize a catalyst, typically platinum or rhodium, to facilitate chemical reactions that break down HCs into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O).
Catalytic converters are highly effective in reducing HC emissions, with conversion rates typically exceeding 90%. They have been widely implemented in vehicles since the 1970s and have played a significant role in improving air quality in urban areas.
Fuel Injection Systems
Fuel injection systems deliver fuel to the engine cylinders more precisely and efficiently compared to carburetors. This results in better fuel combustion, reducing the production of HCs and other pollutants.
Fuel injection systems can be classified into two main types: port fuel injection (PFI) and direct fuel injection (DFI). PFI injects fuel into the intake manifold, while DFI injects fuel directly into the combustion chamber. Both systems offer improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions compared to carburetors.
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems redirect a portion of the exhaust gases back into the engine’s intake manifold. This helps to reduce combustion temperatures, which in turn lowers the formation of HCs and nitrogen oxides (NOx).
EGR systems are particularly effective in reducing HC emissions during high-load engine operation, such as when accelerating or climbing hills. However, they can also lead to increased particulate matter (PM) emissions, which must be considered when designing and implementing EGR systems.
Lean-Burn Engines
Lean-burn engines operate with a higher air-to-fuel ratio compared to conventional engines. This leaner mixture reduces the amount of fuel available for combustion, resulting in lower HC emissions.
Lean-burn engines can achieve significant reductions in HC emissions, but they may also experience higher NOx emissions. Therefore, they often require additional emission control technologies, such as catalytic converters or EGR systems, to meet emission standards.
Alternative Fuels
Alternative fuels, such as natural gas, propane, and biofuels, can produce lower HC emissions compared to gasoline or diesel fuel. These fuels have different combustion characteristics that result in reduced HC formation.
The use of alternative fuels can be particularly beneficial in heavy-duty vehicles, such as trucks and buses, which contribute a significant portion of HC emissions in urban areas.
Technological Advancements for HC Reduction
Recent technological advancements have revolutionized the automotive industry, leading to significant reductions in HC emissions. These advancements have focused on improving engine efficiency, combustion processes, and emission control systems.
One notable advancement is the implementation of electronic fuel injection (EFI) systems. EFI precisely controls the fuel delivery to the engine, optimizing the air-fuel ratio for cleaner combustion. This results in a significant reduction in unburned hydrocarbons released into the atmosphere.
Catalytic Converters
Catalytic converters are essential components of modern exhaust systems that play a crucial role in reducing HC emissions. These devices contain a catalyst, typically platinum or palladium, which promotes chemical reactions that convert harmful pollutants into less harmful substances.
- Three-Way Catalytic Converters (TWCs):TWCs simultaneously reduce HC, CO, and NOx emissions by converting them into carbon dioxide, water, and nitrogen.
- Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR):SCR systems use urea or ammonia to convert NOx into nitrogen and water. This technology is particularly effective in reducing NOx emissions from diesel engines.
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
EGR systems recirculate a portion of the exhaust gases back into the engine’s intake manifold. This reduces the combustion temperature, which in turn suppresses the formation of NOx and HC emissions.
Variable Valve Timing (VVT)
VVT systems optimize the timing of the engine’s valves to improve engine efficiency and reduce emissions. By adjusting the valve timing, the engine can operate more efficiently, resulting in lower HC emissions.
Hybrid and Electric Vehicles
Hybrid and electric vehicles offer a promising solution for reducing HC emissions. These vehicles rely on electric motors or a combination of electric and internal combustion engines, significantly reducing or eliminating tailpipe emissions.
Best Practices for HC Emission Control
To effectively control HC emissions, implementing best practices is crucial. These practices encompass a range of strategies and technologies that can be tailored to specific industries and processes.
The benefits of implementing these practices are multifaceted. They include reducing air pollution, improving public health, enhancing energy efficiency, and potentially reducing operational costs. However, challenges may arise during implementation, such as capital investment, technical complexity, and potential trade-offs with other environmental objectives.
Industrial Practices
In various industries, specific best practices have emerged to control HC emissions. In the automotive industry, for example, catalytic converters and fuel injection systems play a vital role in reducing HC emissions from vehicles.
Operational Practices
Operational practices can also significantly impact HC emissions. Proper maintenance of equipment, such as regular tune-ups and inspections, can help minimize HC leaks and improve combustion efficiency. Additionally, optimizing process parameters, such as temperature and pressure, can further reduce HC emissions.
Emerging Technologies
Technological advancements offer promising solutions for HC emission control. Advanced combustion technologies, such as lean burn engines and gas turbines, can achieve high combustion efficiency with reduced HC emissions. Furthermore, the use of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, can eliminate HC emissions associated with fossil fuel combustion.
Case Studies and Success Stories: Tricks To Lower Hc Emissions
Numerous organizations have made significant strides in reducing HC emissions, showcasing the effectiveness of various strategies and techniques.
One notable example is Ford Motor Company, which implemented a comprehensive program to reduce HC emissions from its manufacturing facilities. By adopting innovative technologies, optimizing processes, and enhancing employee training, Ford achieved a 90% reduction in HC emissions over a decade.
Case Study: Ford Motor Company
- Strategies:Adoption of low-VOC paints, solventless adhesives, and improved leak detection systems.
- Techniques:Process optimization, employee training, and regular monitoring to ensure compliance.
- Results:A 90% reduction in HC emissions from manufacturing facilities over a decade.
Policy and Regulatory Measures

Governments worldwide have implemented various policies and regulations to curb HC emissions, ranging from emission standards to fuel quality regulations and economic incentives. These measures aim to reduce HC emissions from vehicles, industrial processes, and other sources.
One way to reduce HC emissions is to use lean-burn engines. These engines operate with a higher air-to-fuel ratio, which results in more complete combustion and lower HC emissions. If you’re looking for more information on this topic, check out the tissues chapter 5 answer key . It’s a great resource for learning about the different types of engines and how they operate.
Continuing with our discussion on lowering HC emissions, another effective technique is to use catalytic converters. These devices convert harmful pollutants into less harmful substances, further reducing HC emissions and improving air quality.
Emission standards set limits on the amount of HC that can be emitted by vehicles, often expressed in grams per kilometer or mile. Fuel quality regulations mandate the use of cleaner fuels, such as low-sulfur gasoline and diesel, which produce fewer HC emissions during combustion.
Effectiveness and Challenges
These measures have been effective in reducing HC emissions, particularly in developed countries. However, challenges remain, especially in developing countries where enforcement of regulations may be weaker and older vehicles with higher emissions are still in use.
One challenge is the cost of implementing and enforcing regulations, particularly for small businesses and developing countries. Another challenge is the need for ongoing technological advancements to meet increasingly stringent emission standards.
Economic Considerations
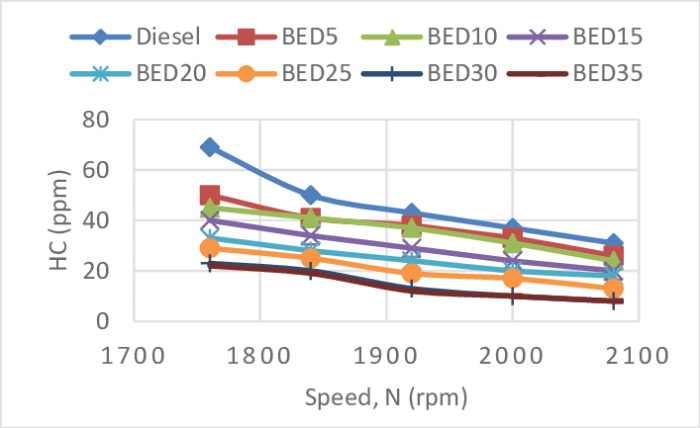
Reducing HC emissions requires significant financial investment and strategic planning. The costs associated with implementing emission control strategies vary depending on the specific technologies and approaches adopted. These costs may include capital investments in equipment, maintenance and operating expenses, and research and development.
Cost-Benefit Analysis, Tricks to lower hc emissions
Organizations and policymakers must carefully consider the costs and benefits of HC emission reduction efforts. Benefits include improved public health, reduced environmental damage, and potential economic gains from increased energy efficiency and innovation. A thorough cost-benefit analysis can help determine the most cost-effective and sustainable strategies for achieving HC emission reduction goals.
Essential FAQs
What are the major sources of HC emissions?
HC emissions primarily originate from combustion processes, including motor vehicles, industrial activities, and power generation.
How do HC emissions impact the environment?
HC emissions contribute to smog formation, ozone depletion, and climate change, harming air quality and ecosystems.
What are some effective methods for reducing HC emissions?
Effective methods include catalytic converters, fuel injection systems, and cleaner production technologies in industries.