How do you calculate weeks of supply? This question lies at the heart of effective inventory management, enabling businesses to optimize their supply chains, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of weeks of supply (WoS) calculations, exploring its significance, formula, influencing factors, and practical applications.
WoS is a crucial metric that measures the duration of time that an organization can meet demand with its current inventory levels. Understanding how to calculate WoS empowers businesses to strike a delicate balance between overstocking and stockouts, ensuring uninterrupted operations and maximizing profitability.
Understanding Weeks of Supply (WoS): How Do You Calculate Weeks Of Supply
Weeks of Supply (WoS) is a critical metric in inventory management that measures the number of weeks a company can meet demand with its current inventory levels. It provides insights into the adequacy of inventory and helps optimize supply chain operations.
Formula for Calculating WoS
WoS is calculated using the following formula:
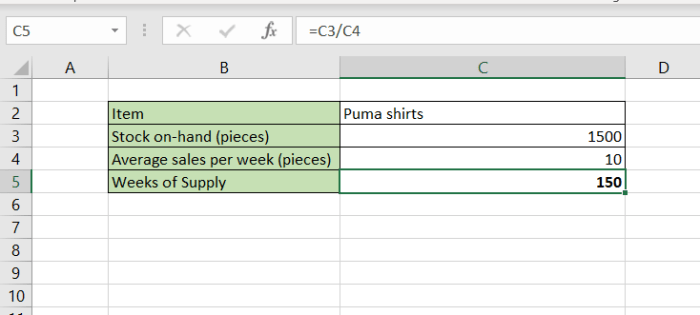
WoS = (Current Inventory / Average Weekly Demand)
Where:
- Current Inventory: The total inventory on hand at the time of calculation.
- Average Weekly Demand: The average weekly demand for the product over a specific period.
Factors Influencing WoS
Several factors can influence WoS calculations, including:
- Demand Variability: Changes in demand patterns can affect WoS calculations.
- Lead Time: The time it takes to replenish inventory can impact WoS.
- Safety Stock: The amount of extra inventory held to buffer against unexpected demand or supply disruptions.
Methods for Calculating WoS, How do you calculate weeks of supply
There are several methods for calculating WoS, including:
- Historical Data Method: Uses historical demand data to estimate average weekly demand.
- Forecast-Based Method: Uses demand forecasts to estimate average weekly demand.
- Time-Phased Method: Considers the timing of demand and inventory replenishment.
WoS Analysis and Interpretation
Analyzing WoS calculations helps identify potential inventory issues. High WoS values indicate excess inventory, while low WoS values indicate potential stockouts. Optimal WoS values vary by industry and product.
Applications of WoS in Inventory Management
WoS is a valuable tool for optimizing inventory management. It helps:
- Maintain appropriate inventory levels to meet demand.
- Reduce inventory holding costs.
- Improve customer service by minimizing stockouts.
Detailed FAQs
What is the formula for calculating weeks of supply?
WoS = (Current Inventory / Average Weekly Demand)
How do I interpret weeks of supply values?
High WoS values indicate excess inventory, while low values suggest potential stockouts. Aim for a balance that meets demand without excessive carrying costs.
What factors influence weeks of supply?
Demand variability, lead times, safety stock levels, and production capacity are key factors that impact WoS calculations.
How can I use weeks of supply to optimize inventory levels?
WoS analysis helps determine optimal inventory levels to minimize carrying costs, reduce stockouts, and improve customer service.