Which of these hazmat products are allowed in your fc – In the realm of fulfillment centers (FCs), handling hazardous materials (Hazmats) requires utmost caution and adherence to regulatory guidelines. This article delves into the crucial question of which Hazmat products are permissible within FCs, exploring the prohibited and allowed categories, storage and handling requirements, training and compliance measures, and hazard communication protocols.
Understanding these aspects is paramount for ensuring the safety of employees, protecting the environment, and maintaining compliance with industry regulations. As we navigate through this comprehensive guide, you will gain valuable insights into managing Hazmat products effectively within your FC.
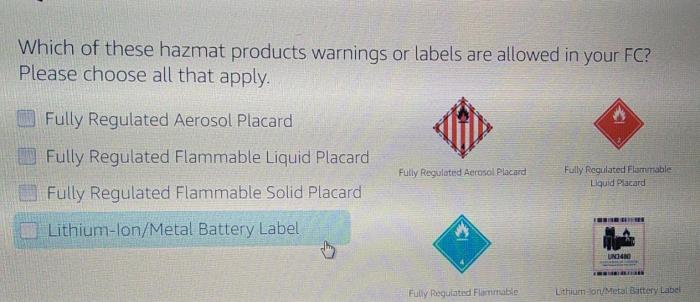
1. Identify Prohibited and Allowed Hazmat Products

Fulfillment centers (FCs) must adhere to strict regulatory guidelines and standards when handling hazardous materials (Hazmats). These regulations aim to ensure the safety of employees, customers, and the environment. Understanding which Hazmat products are prohibited and allowed in FCs is crucial for compliance and risk mitigation.
Prohibited Hazmat Products
- Explosives (e.g., fireworks, ammunition)
- Flammable liquids (e.g., gasoline, acetone)
- Corrosive substances (e.g., acids, bases)
- Toxic substances (e.g., pesticides, heavy metals)
- Radioactive materials (e.g., nuclear waste, medical isotopes)
Allowed Hazmat Products
- Consumer products (e.g., cleaning supplies, batteries)
- Industrial chemicals (e.g., solvents, adhesives)
- Pharmaceuticals (e.g., prescription drugs, vaccines)
Allowed Hazmat products may have specific conditions or restrictions for their storage and handling. These conditions may include:
- Limited quantities
- Specific storage areas
- Proper labeling and signage
2. Assess Storage and Handling Requirements
Proper storage and handling of Hazmat products are essential for safety and compliance. FCs must implement measures to minimize risks associated with these materials.
Storage Conditions
- Temperature control
- Ventilation
- Segregation from incompatible materials
Safety Protocols
- Personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Spill containment
- Emergency response procedures
Disposal and Recycling, Which of these hazmat products are allowed in your fc
- Adhering to environmental regulations
- Following industry best practices
3. Establish Training and Compliance Measures

Training and compliance measures are crucial for ensuring the safe handling of Hazmat products in FCs. Employees must be adequately trained and regularly audited to maintain compliance.
Training Requirements
- Product identification
- Safe handling techniques
- Emergency response
Safety Audits and Inspections
- Regular inspections of storage areas
- Review of safety protocols
- Assessment of employee training
Documentation and Record-Keeping
- Accurate documentation of Hazmat handling
- Maintenance of Safety Data Sheets (SDSs)
- Record-keeping of disposal and recycling activities
4. Implement Hazard Communication and Labeling

Effective hazard communication is vital for informing employees and emergency responders about potential risks associated with Hazmat products. FCs must implement measures to ensure clear and accurate communication.
Safety Data Sheets (SDSs)
- Availability and accessibility
- Detailed information on product hazards
- Emergency response guidelines
Proper Labeling and Signage
- Globally Harmonized System (GHS) standards
- Hazard pictograms and signal words
- Clear and concise labeling
Hazard Communication Training
- Understanding of SDSs
- Recognition of hazard pictograms
- Appropriate response measures
Essential FAQs: Which Of These Hazmat Products Are Allowed In Your Fc
What are the primary regulatory guidelines for handling Hazmats in FCs?
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) provide comprehensive regulations for handling Hazmats, including storage, labeling, and emergency response procedures.
What are the consequences of non-compliance with Hazmat regulations?
Non-compliance can lead to fines, legal penalties, and reputational damage. It also poses significant risks to employee safety and environmental well-being.
How often should safety audits and inspections be conducted?
Regular audits and inspections are essential to ensure ongoing compliance. The frequency should be determined based on the specific Hazmats handled, the volume of operations, and the regulatory requirements.