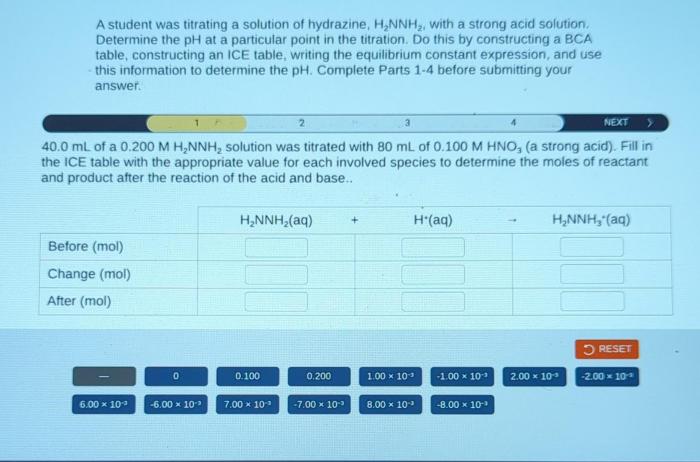
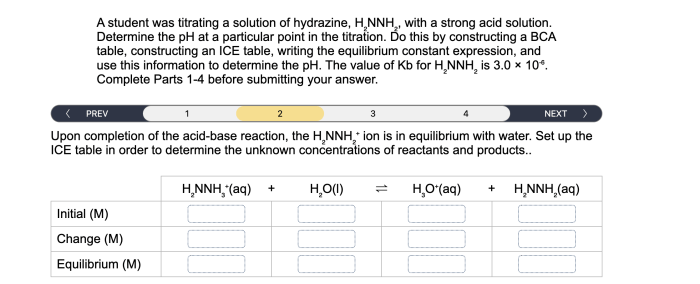
A student was titrating a solution of hydrazine, embarking on a scientific journey to determine its concentration. This experiment, rooted in the principles of analytical chemistry, unveils the significance of titration in understanding the properties and applications of this intriguing compound.
Hydrazine, a colorless liquid with a pungent odor, possesses unique chemical characteristics that make it a valuable substance in various industries. Its reactivity and stability demand careful handling, necessitating an in-depth understanding of its properties and the safety precautions required for its use.
Titration of Hydrazine Solution: A Student Was Titrating A Solution Of Hydrazine
Titration is a fundamental analytical technique in chemistry used to determine the concentration of a known solution by reacting it with a solution of known concentration. In the case of hydrazine, a solution of known concentration is added to a solution of hydrazine until the reaction is complete, as indicated by a change in color or other observable property.
The steps involved in titrating a solution of hydrazine include:
- Preparing a solution of known concentration.
- Measuring a known volume of the hydrazine solution into a flask.
- Adding the titrant solution slowly from a burette while swirling the flask.
- Monitoring the reaction using an indicator or other suitable method.
- Recording the volume of titrant added when the endpoint is reached.
The equipment used in the titration process includes a burette, flask, indicator, and measuring devices.
Properties of Hydrazine
Hydrazine is a colorless, fuming liquid with a pungent odor. It is highly reactive and unstable, and can decompose violently if not handled properly. The physical and chemical properties of hydrazine include:
- Molecular formula: N2H4
- Molecular weight: 32.05 g/mol
- Density: 1.008 g/cm3
- Boiling point: 113.5 °C
- Melting point: 2.0 °C
- Solubility in water: Miscible
- Acidity: Weak base
- Reactivity: Highly reactive
Hydrazine is a strong reducing agent and can react violently with oxidizing agents. It is also corrosive to metals and can cause severe burns to the skin and eyes. Due to its hazardous nature, hydrazine must be handled with extreme care and appropriate safety precautions must be taken.
Applications of Hydrazine
Hydrazine has a wide range of industrial and scientific applications, including:
- Rocket propulsion:Hydrazine is used as a fuel in rocket engines, providing high thrust and specific impulse.
- Fuel cells:Hydrazine is used as a fuel in fuel cells, producing electricity through a chemical reaction with oxygen.
- Pharmaceutical industry:Hydrazine is used as an intermediate in the synthesis of various pharmaceuticals, including anti-depressants and anti-psychotics.
- Corrosion inhibitor:Hydrazine is used as a corrosion inhibitor in boilers and steam systems.
- Water treatment:Hydrazine is used as a reducing agent in water treatment, removing dissolved oxygen and preventing corrosion.
Hydrazine’s unique properties make it a valuable compound in various industries, but its hazardous nature requires careful handling and strict adherence to safety protocols.
Analytical Techniques
The concentration of hydrazine in a solution can be determined using various analytical techniques, including:
- Potentiometric titration:This technique involves measuring the change in electrical potential between two electrodes as the titrant is added. The endpoint is reached when the potential reaches a predetermined value.
- Spectrophotometry:This technique involves measuring the absorbance of light at a specific wavelength as the titrant is added. The endpoint is reached when the absorbance reaches a maximum or minimum value.
Each technique has its own advantages and limitations, and the choice of technique depends on factors such as the accuracy, precision, and sensitivity required.
Data Analysis
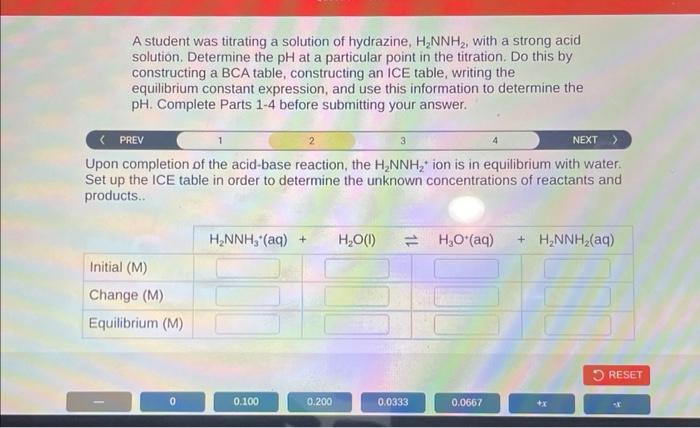
Analyzing titration data to determine the concentration of hydrazine involves the following steps:
- Plotting the titration curve:A graph is plotted with the volume of titrant added on the x-axis and the observed property (e.g., pH, absorbance) on the y-axis.
- Determining the endpoint:The endpoint is the point on the titration curve where the reaction is complete. This can be determined visually or mathematically.
- Calculating the concentration:The concentration of hydrazine can be calculated using the formula: Concentration = (Volume of titrant × Concentration of titrant) / Volume of sample
Accurate measurements and proper data handling are crucial to ensure the reliability of the results. Statistical methods can be used to evaluate the uncertainty and precision of the measurements.
FAQ Explained
What is the purpose of titrating a solution of hydrazine?
Titrating a solution of hydrazine allows for the determination of its concentration, which is crucial for understanding its properties and applications.
What safety precautions should be taken when handling hydrazine?
Hydrazine is a toxic and corrosive substance, requiring proper handling and storage. Personal protective equipment, such as gloves and goggles, should be worn, and the experiment should be conducted in a well-ventilated area.
What are the industrial applications of hydrazine?
Hydrazine is used as a rocket propellant, in fuel cells, and in the production of pharmaceuticals and pesticides.