Activity 16.3 locate the epicenter of an earthquake – In the realm of seismology, understanding the epicenter of an earthquake is paramount. Activity 16.3: Locate the Epicenter of an Earthquake delves into the methods and significance of determining the precise location where seismic energy originates, providing a comprehensive exploration of this fundamental concept.
By unraveling the principles of triangulation, array analysis, and real-time monitoring systems, this activity empowers individuals with the knowledge and techniques to pinpoint the epicenter of earthquakes. This understanding not only enhances our comprehension of earthquake behavior but also plays a crucial role in hazard assessment, source mechanism analysis, and early warning systems.
Understanding the Epicenter: Activity 16.3 Locate The Epicenter Of An Earthquake
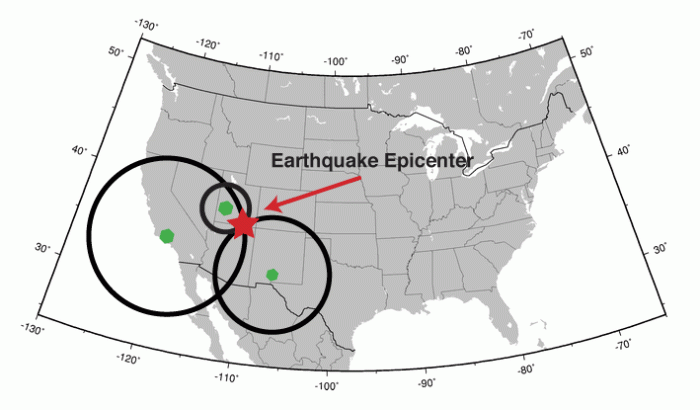
An earthquake’s epicenter is the point on the Earth’s surface directly above the hypocenter, the point within the Earth where the earthquake rupture begins. The epicenter is a critical location for understanding earthquake behavior, as it represents the point from which seismic energy radiates outward.
Methods for Locating the Epicenter
Triangulation Method
Triangulation is a geometric technique used to determine the location of the epicenter. By measuring the time difference between the arrival of seismic waves at three or more seismic stations, the distance from each station to the epicenter can be calculated.
The intersection of these distances provides an estimate of the epicenter’s location.
Triangulation is a relatively simple and accurate method for locating the epicenter, but it requires a minimum of three seismic stations with known locations.
Data Collection and Analysis
To locate the epicenter of an earthquake, several types of data are needed, including:
- Seismic wave arrival times at multiple seismic stations
- Waveform characteristics, such as amplitude and frequency
- Geological and tectonic information about the region
Seismic data is collected using seismometers, which are instruments that measure ground motion. The data is then processed and analyzed using specialized software to determine the epicenter’s location.
Advanced Techniques
Array Analysis
Array analysis involves using a group of closely spaced seismic sensors to improve the accuracy of epicenter location. By analyzing the subtle differences in the arrival times of seismic waves at each sensor, it is possible to determine the direction from which the waves are coming.
This information can be used to refine the epicenter’s location.
Array analysis is particularly useful for locating earthquakes in complex geological regions, where traditional triangulation methods may be less accurate.
Real-Time Monitoring Systems, Activity 16.3 locate the epicenter of an earthquake
Real-time earthquake monitoring systems use advanced technology to rapidly detect and locate earthquakes. These systems typically consist of a network of seismic stations that transmit data to a central processing center. The data is processed in real-time to determine the earthquake’s magnitude, location, and other parameters.
Real-time monitoring systems are essential for earthquake early warning systems, which provide critical seconds of warning before an earthquake’s arrival.
Applications and Impact
Locating the epicenter of an earthquake has several important applications, including:
- Earthquake hazard assessment:The epicenter’s location can be used to estimate the intensity of ground shaking in different areas, which is essential for seismic hazard maps.
- Understanding earthquake source mechanisms:The epicenter’s location can provide insights into the type of fault that caused the earthquake and the direction of rupture.
- Earthquake early warning systems:Real-time epicenter location is crucial for earthquake early warning systems, which can provide valuable seconds of warning before an earthquake’s arrival.
Query Resolution
What is the significance of locating the epicenter of an earthquake?
Determining the epicenter provides valuable information for understanding earthquake behavior, assessing seismic hazards, analyzing source mechanisms, and implementing early warning systems.
How does triangulation help in locating the epicenter?
Triangulation involves using the time difference between seismic wave arrivals at multiple stations to calculate the distance to the epicenter. By combining measurements from several stations, the epicenter can be precisely located.
What are the advantages of using array analysis for epicenter location?
Array analysis utilizes multiple seismic sensors arranged in a specific pattern to enhance signal-to-noise ratio and improve the accuracy of epicenter determination, especially for smaller earthquakes.
How do real-time monitoring systems contribute to epicenter location?
Real-time monitoring systems provide continuous data from seismic networks, allowing for rapid and accurate epicenter determination. This enables timely warnings and response efforts during earthquake events.